Comment le kit de cathéter veineux central atteint-il des objectifs médicaux grâce à la synergie de divers composants?
Analyse des composants principaux du kit
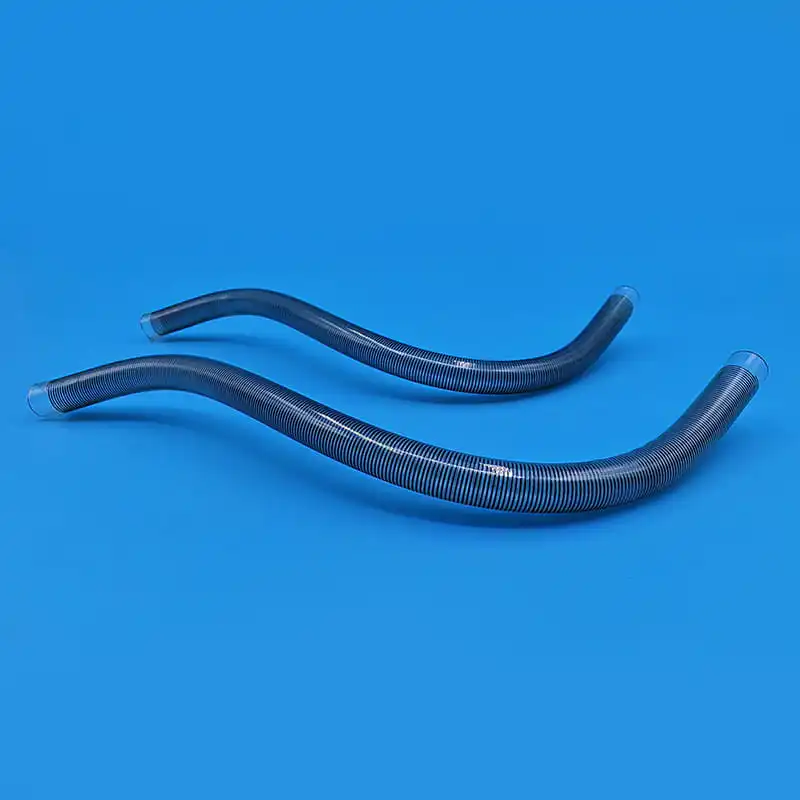
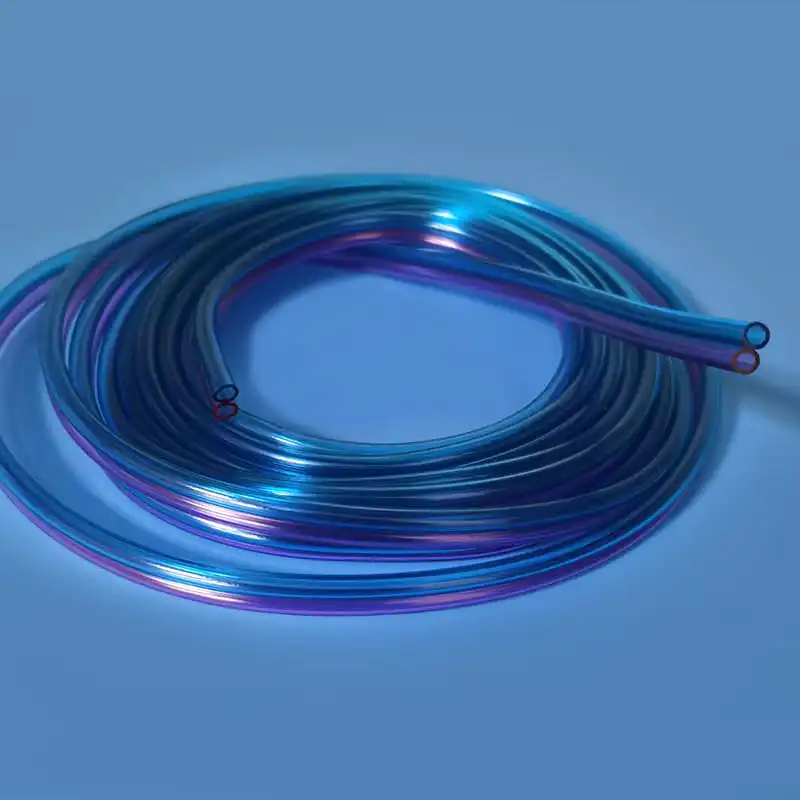
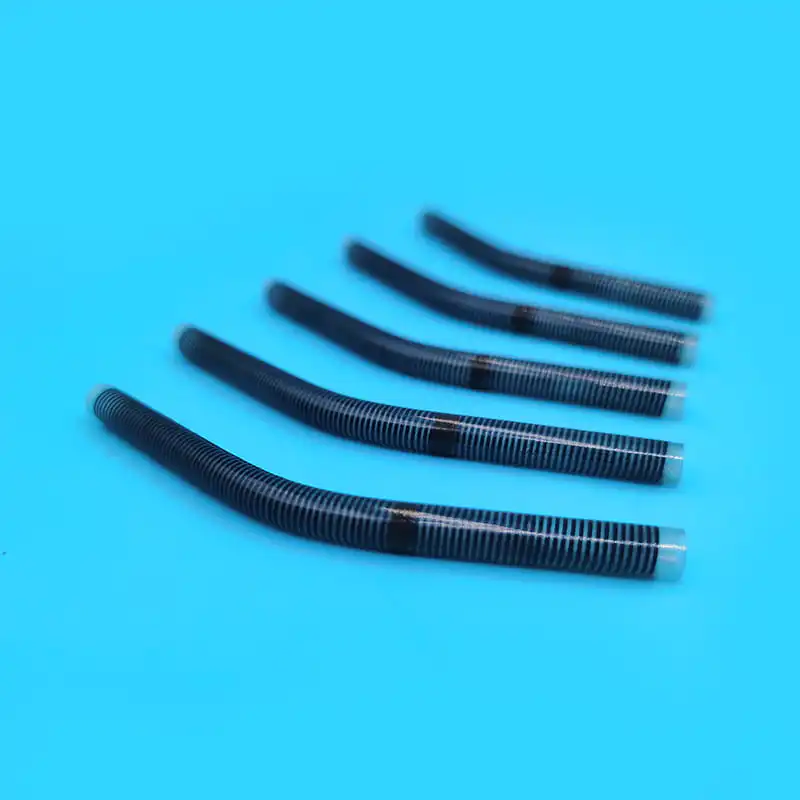
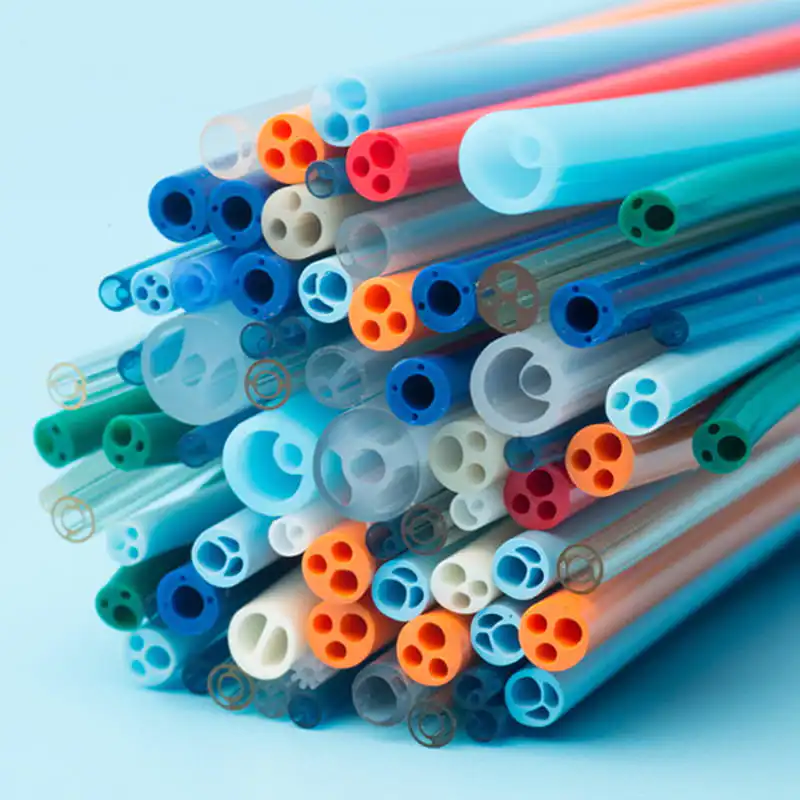
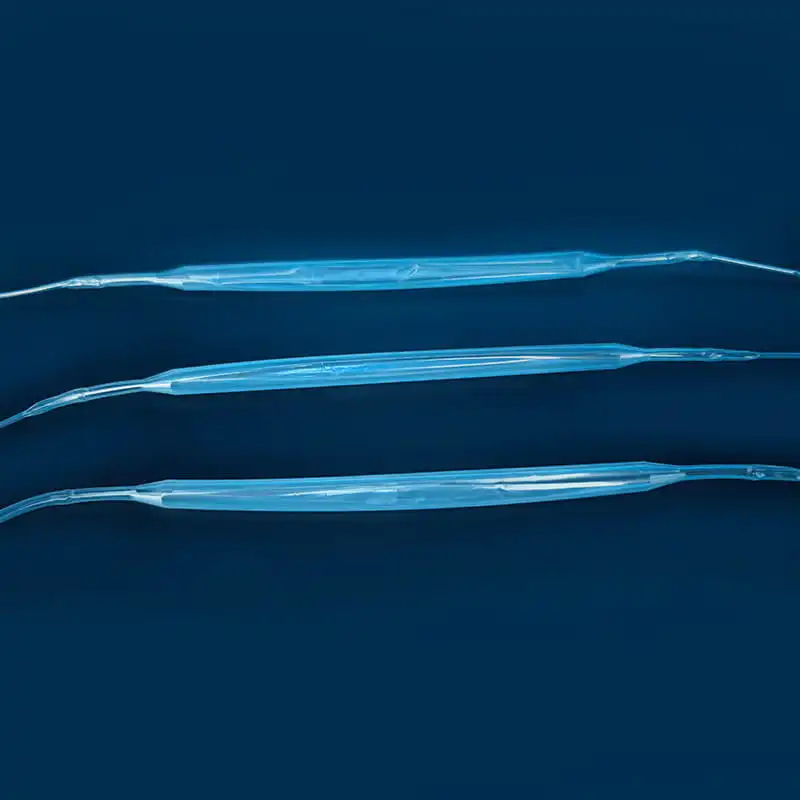
Le kit de cathéter veineux central Contient une variété de composants clés, chacun jouant un rôle unique et irremplaçable dans l'ensemble du processus d'opération médicale. Le premier est le cathéter veineux central, qui est le composant central du kit et est le canal reliant la veine centrale à l'extérieur du corps et à l'intérieur du corps. Son matériau est généralement en polyuréthane de qualité médicale ou en silicone. Ces matériaux ont une bonne biocompatibilité et peuvent réduire efficacement le rejet par le corps des corps étrangers et réduire le risque de complications telles que l'infection. Différents types de cathéters veineux centraux ont leurs propres caractéristiques dans la structure et la fonction. Les cathéters à l'écart unique conviennent aux besoins de traitement unique, tandis que les cathéters à double lumen ou multi-combats peuvent effectuer une variété d'opérations médicales différentes en même temps, telles que la perfusion, la collecte de sang et l'administration de médicaments, ce qui améliore considérablement l'efficacité et la commodité des opérations médicales. En termes de conception, certaines surfaces de cathéter sont traitées avec des revêtements spéciaux pour améliorer encore les propriétés anti-thrombotiques; Certains sont également marqués d'échelles pour faciliter le personnel médical pour saisir avec précision la profondeur d'insertion.
Le cannula plays a pioneering role in the central venous catheter kit. When performing a central venous catheter insertion operation, the cannula is first used for percutaneous puncture into the vein. Its needle tip adopts a bevel cutting process. This design is sharp and precise, and can quickly and accurately penetrate the skin and vein wall with minimal resistance, opening a channel for the entry of subsequent components. The needle core and outer sleeve of the cannula needle are closely matched. When the cannula needle successfully enters the vein, the inner needle core is removed through a special separation mechanism, and the outer sleeve with a certain hardness and flexibility will remain in the vein as a guide channel for subsequent guide wires and other components to enter. To ensure the accuracy of puncture, some cannula needles are also equipped with ultrasound guidance adapters, which can be used with ultrasound equipment to observe the puncture path and blood vessel status in real time.
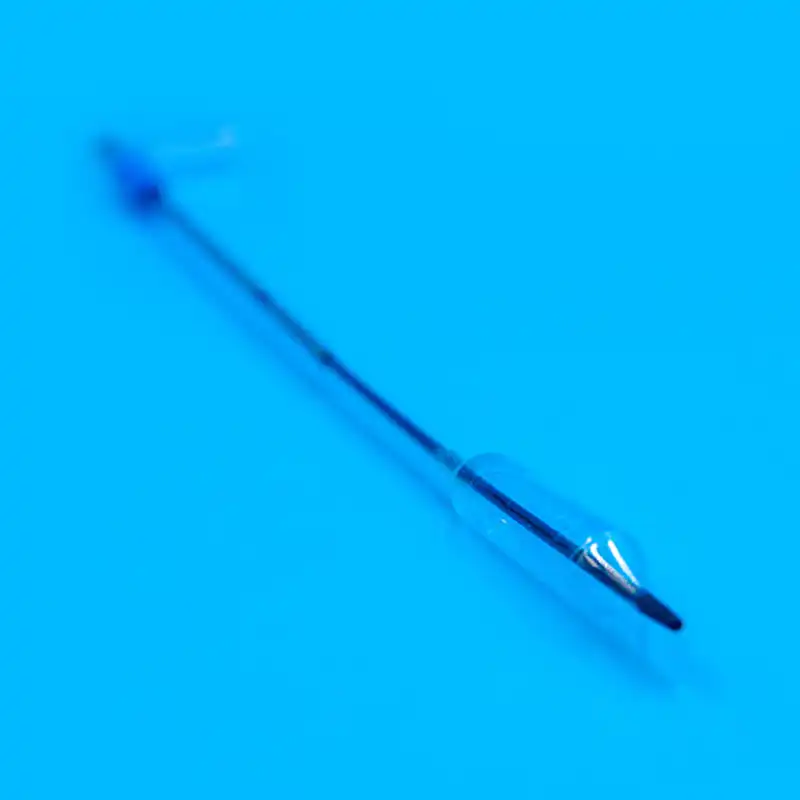
Le guidewire is a key tool for precise positioning and guidance in the central venous catheter kit. After the cannula needle establishes the initial channel, the guidewire will be sent into the vein through the cannula. The outer layer of the guidewire is usually woven from medical-grade stainless steel wire, and the inner layer is a nickel-titanium alloy core. This structure gives the guidewire good flexibility and maneuverability. Doctors can use the J-shaped or straight head design of the guidewire tip to flexibly turn and guide it in the blood vessel through in vitro operation, and accurately send it to the target position. Some high-end guidewires also have a hydrophilic coating, which becomes lubricated after contact with blood, further reducing friction damage to the inner wall of the blood vessel. The existence of the guidewire makes the insertion path of the central venous catheter clearer and more controllable, laying a solid foundation for the smooth insertion of the subsequent catheter.
Le role of the dilator in the central venous catheter kit should not be ignored. Since the diameter of the vein is relatively thin, and the central venous catheter needs to be smoothly inserted, it is necessary to properly dilate the vein. The dilator usually adopts a conical or cylindrical design, and the material is mostly medical-grade polyethylene. It can enter the vein along the guidewire and expand the channel of the venous puncture site by gradually expanding. During the expansion process, the smooth surface treatment and gradual caliber design of the dilator can reduce damage to the venous tissue while ensuring effective expansion. For special patients, such as those with thin blood vessel walls or sclerosis, there are also special controllable dilators available, and doctors can accurately adjust the expansion strength and range according to actual conditions.
Le peelable sheath is an important part of the central venous catheter kit to ensure the safe insertion of the catheter. After the dilator completes the dilation of the vein, the peelable sheath will be sent into the vein along the guidewire and dilator. The peelable sheath consists of two symmetrical half sheaths connected by a special locking structure in the middle. When the peelable sheath reaches the appropriate position, the central venous catheter will be inserted into the vein through the sheath. At this time, the medical staff will separate the peelable sheath from the middle lock and remove it from the body through a specific operation technique, while the central venous catheter will be left in the vein. This unique design not only ensures the smooth catheter insertion process, but also avoids unnecessary damage to the vein and catheter. To prevent accidental scratches on the surrounding tissue when the sheath is peeled off, the edge of the sheath is specially rounded and blunted.
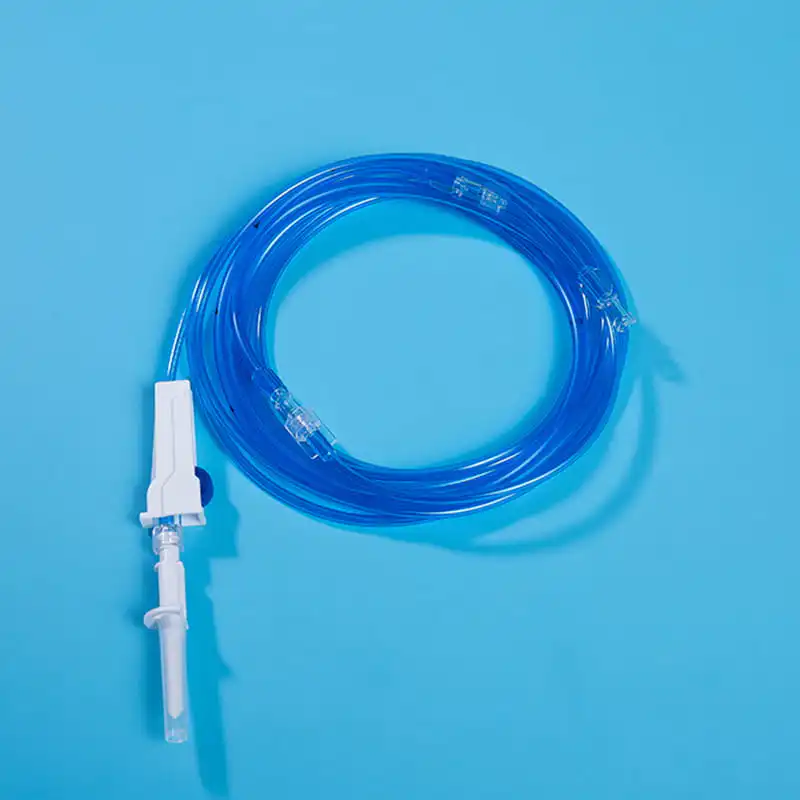
Le fixing device plays a role in stabilizing and fixing the catheter in the central venous catheter kit. In order to ensure that the central venous catheter can maintain a stable position in the patient's body for a long time without displacement or falling off, fixing devices such as sutures, sterile dressings or special catheter fixers will be used to fix the catheter to the patient's skin. The suture fixation method is suitable for patients with long-term catheterization. The catheter is fixed to the skin tissue through delicate suturing operations; the sterile dressing is breathable, waterproof and antibacterial, and can effectively protect the puncture site; the dedicated catheter fixator is made of medical-grade silicone or polymer materials, and can be personalized according to the patient's skin morphology and catheter model through an adjustable buckle design. Appropriate fixation can not only ensure the normal function of the catheter, but also reduce the discomfort and potential risks caused to the patient by the movement of the catheter.
Le interface for external connection is the bridge between the central venous catheter and external medical equipment. Through these interfaces, the central venous catheter can be connected to infusion sets, syringes and other equipment to achieve various medical operations such as infusion, drug administration, and blood collection. The design of these interfaces has good sealing and compatibility, and common ones include Luer connectors and needleless infusion connectors. The Luer connector is connected by threads to ensure a tight connection without leakage; the needleless infusion connector adopts a diaphragm design, which can complete the infusion operation without acupuncture, reducing the risk of infection. At the same time, some interfaces also have anti-backflow function to prevent blood from reflux and blocking the catheter, and support multiple devices to be connected at the same time to meet complex clinical needs.
Large gamme de scénarios d'application clinique
Dans les applications médicales réelles, les scénarios d'utilisation des kits de cathéter veineux centraux sont très larges. Dans le domaine des soins intensifs, pour les patients souffrant de conditions critiques qui ont besoin d'une grande quantité de perfusion et de médicaments fréquents, les cathéters veineux centraux peuvent fournir un canal de perfusion rapide et stable pour répondre aux besoins des patients en liquides et en médicaments. En prenant des patients avec un choc septique à titre d'exemple, pendant le processus de sauvetage, une grande quantité de liquide cristalloïde, de liquide colloïde et de médicaments vasoactifs doit être complété dans un court laps de temps. Le cathéter veineux central peut s'assurer que ces fluides et médicaments entrent rapidement dans la circulation sanguine et corriger rapidement l'état de choc. Dans le même temps, la surveillance hémodynamique peut également être effectuée via le cathéter veineux central. Le médecin relie le capteur de pression à l'interface du cathéter pour obtenir des paramètres tels que la pression veineuse centrale et la pression du coin de l'artère pulmonaire en temps réel, ce qui aide les médecins à comprendre la fonction cardiaque du patient et l'état de la circulation sanguine en temps réel et fournit une base importante pour formuler des plans de traitement précis.
Dans le traitement tumoral, de nombreux médicaments de chimiothérapie sont très irritants pour les vaisseaux sanguins, et l'administration par des veines périphériques peut provoquer des complications telles que la phébite. Le kit de cathéter veineux central peut placer un cathéter dans la veine centrale, permettant aux médicaments de chimiothérapie d'entrer directement dans les grands vaisseaux sanguins et d'être rapidement dilués, réduisant ainsi l'irritation aux vaisseaux sanguins, réduisant la probabilité de complications et améliorant la tolérance et la conformité du traitement des patients. Par exemple, les patientes atteintes d'un cancer du sein qui reçoivent des médicaments de chimiothérapie très irritants tels que la doxorubicine peuvent utiliser des cathéters veineux centraux pour éviter efficacement de graves conséquences telles que la nécrose cutanée et l'ulcération tissulaire causée par l'extravasation du médicament. Dans le même temps, pour les patients qui ont besoin d'une chimiothérapie à long terme et multiple, les cathéters veineux centraux réduisent la douleur des perforations répétées et améliorent la continuité du traitement.
De plus, dans la thérapie de soutien nutritionnel, les cathéters veineux centraux peuvent être utilisés pour le soutien total de la nutrition parentérale pour les patients qui ne peuvent pas absorber suffisamment de nutrition via le tractus gastro-intestinal, comme les patients atteints de coma à long terme et de brûlures graves. Donner une solution de nutriments à haute concentration et à haut calorie à travers la veine centrale peut répondre aux besoins du corps du patient en nutriments et favoriser la récupération du patient. Prenant l'exemple des patients avec des brûlures étendues, leur fonction gastro-intestinale est supprimée en raison d'un traumatisme, et ils ne peuvent pas digérer et absorber les aliments normalement. À l'heure actuelle, la solution nutritive tout-en-un contenant des acides aminés, une émulsion de graisse, du glucose et d'autres ingrédients est donnée à travers le cathéter veineux central pour maintenir l'équilibre de l'azote du patient, reconstituer l'énergie requise par le corps et accélérer la cicatrisation des plaies. Dans le même temps, le personnel médical peut également surveiller les électrolytes du patient, la glycémie et d'autres indicateurs à travers le cathéter veineux central et ajuster le plan de soutien nutritionnel dans le temps.
Procédures d'exploitation strictes et standardisées
Le operating procedures of the central venous catheter kit need to strictly follow the specifications and standards. Before the operation, the doctor needs to conduct a comprehensive assessment of the patient's condition, including the patient's age, weight, underlying diseases, coagulation function, etc., and select the appropriate puncture site and central venous catheter type. Common puncture sites include the internal jugular vein, subclavian vein and femoral vein. Different sites have their own advantages and disadvantages, and they need to be carefully selected according to the specific situation of the patient. At the same time, detailed explanations and communication should be given to the patient, and the patient should be informed of the operation process, possible risks and key points of cooperation to obtain the patient's cooperation. During the operation, the principle of aseptic operation must be strictly followed. The puncture site must be disinfected with iodine more than three times, and the diameter of the disinfection range must not be less than 15 cm. A large sterile sheet must be laid to ensure that the entire operation is carried out in a sterile environment. Then follow the steps of trocar puncture, guide wire insertion, dilation with a dilator, insertion of a removable sheath, insertion of a central venous catheter, fixation of the catheter, and connection of an external interface. Taking internal jugular vein puncture as an example, under ultrasound guidance, after determining the puncture point, the trocar is inserted at an angle of 30-45 degrees. After seeing the blood return, it is confirmed that it is in the vein, and then the subsequent components are inserted according to the process. After the operation is completed, the patient needs to be closely observed and cared for, and the patient must be monitored for complications and treated in a timely manner. This includes observing whether the puncture site is red, swollen, or exuded, and changing the dressing regularly; monitoring the patient's body temperature, blood routine, and other indicators to determine whether an infection has occurred; evaluating the function of the catheter to ensure smooth infusion, blood collection, and other operations.
Défis et risques rencontrés
Bien que les kits du cathéter veineux central jouent un rôle important dans le domaine médical, ils sont également confrontés à certains défis et risques lors de l'utilisation. L'infection est l'une des complications les plus courantes des cathéters veineux centraux. Étant donné que le cathéter est laissé dans le corps pendant longtemps, il est facile pour les bactéries et autres micro-organismes à envahir, provoquant une infection locale ou une infection systémique. Les bactéries entrent principalement dans le corps par colonisation cutanée au site de ponction, la contamination du connecteur du cathéter et la contamination du système de perfusion. La thrombose est également un problème qui ne peut être ignoré. Le cathéter peut stimuler l'endothélium vasculaire dans le vaisseau sanguin, provoquant des changements dans la coagulation sanguine, formant ainsi un thrombus. Une fois que le thrombus tombe, il peut provoquer de graves complications telles que l'embolie pulmonaire. De plus, des problèmes tels que le blocage du cathéter et le déplacement peuvent également affecter l'utilisation normale et l'effet de traitement du cathéter veineux central. Le blocage du cathéter peut être causé par le dépôt de médicaments, la coagulation sanguine, etc.; Le déplacement du cathéter peut être lié à des facteurs tels que l'activité inappropriée des patients et la fixation lâche.
Pour plus d'informations, veuillez nous appeler au +86-18913710126 ou nous envoyer un e-mail à [email protected].
Introduction Cathéters médicaux sont des éléments essentiels des soin...
Introduction au matériau PEBAX PEBAX est un élastomère thermoplastique qui combine...
Introduction Dans la pratique médicale, en particulier dans les soins post-chirurg...
Dans le domaine médical, la sécurité, la stabilité et l’efficacité de la transmission des fluides...
Introduction Dans les procédures médicales modernes, en particulier celles impliqu...
Les procédures interventionnelles vasculaires font partie intégrante de la médecine cardiovascula...